Hearing aids have advanced the way hard of hearing individuals experience the world around them. But it have also gave birth to a new debate now! Yes, you heard that Right? We are talking about Digital vs Analog Hearing Aids. Over the years, advancements in technology have transformed these devices from simple sound amplifiers to sophisticated tools capable of enhancing auditory experiences. One of the most significant developments in hearing aid technology has been the shift from analog to digital devices. But are digital hearing aids truly better than their analog counterparts? In this blog, we’ll explore the differences between analog and digital hearing aids, their advantages and disadvantages, and help you determine which option might be best for your needs.
Let’s Dive into this Digital vs Analog Hearing Aids
Before diving into the comparison, it’s essential to understand what analog and digital hearing aids are and how they work.

Analog Hearing Aids
Analog hearing aids have been around for decades and were the standard option before digital technology emerged. These devices work by capturing sound waves through a microphone and converting them into electrical signals. The electrical signals are then amplified and sent to the ear. Analog hearing aids amplify all sounds equally, meaning they don’t differentiate between speech and background noise. While some analog models allow for basic adjustments, they lack the advanced processing capabilities of digital devices.
Key Features of Analog Hearing Aids:

- Continuous Amplification: Amplifies all sounds equally, making it harder to differentiate speech in noisy environments.
- Limited Customization: Manual adjustments are required, with fewer options for tailoring sound profiles.
- Affordability: Analog hearing aids are generally less expensive than digital ones.
- Ease of Use: Simple controls make them user-friendly, especially for individuals who prefer minimal technological complexity.
- Reliability: They are less prone to software issues and can be more reliable in certain situations.
Digital Hearing Aids
Digital hearing aids, on the other hand, use digital signal processing (DSP) technology. When sound enters the device, it is converted into digital data (binary code) and processed by a computer chip. This allows the hearing aid to analyze and manipulate the sound in real-time, enhancing certain frequencies while reducing others. Digital hearing aids can distinguish between speech and background noise, offering a more tailored listening experience. They also come with a range of features, such as Bluetooth connectivity, directional microphones, and customizable settings.
Key Features of Digital Hearing Aids:
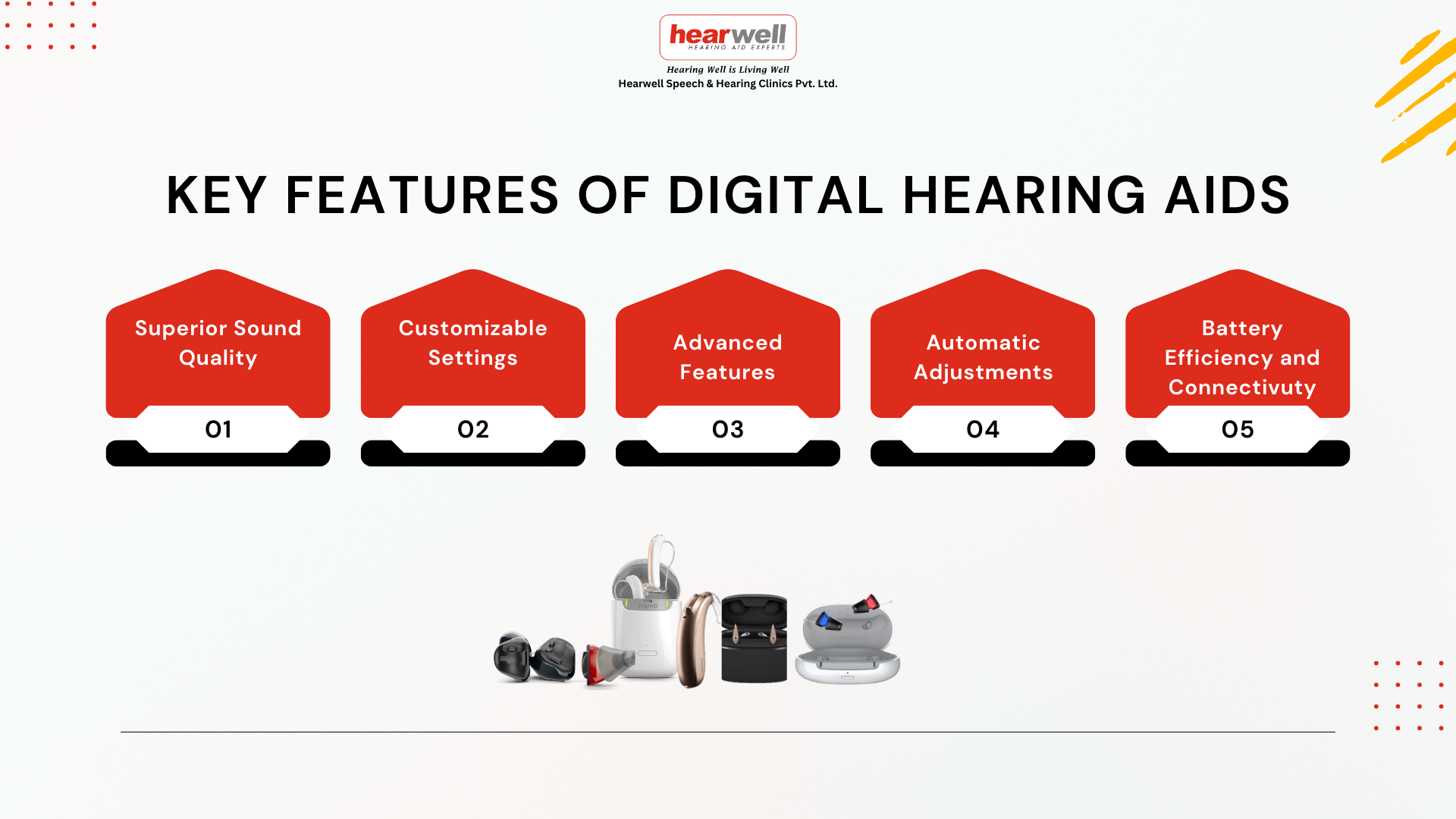
- Superior Sound Quality: Offers advanced noise filtering and speech prioritization for clearer conversations in noisy environments.
- Customizable Settings: Programmable to individual hearing profiles; audiologists can fine-tune them to suit specific needs.
- Advanced Features: Includes directional microphones, feedback cancellation, multiple listening programs, and Bluetooth compatibility.
- Automatic Adjustments: Can adapt to different environments without manual intervention.
- Battery Efficiency: DSP technology often results in longer battery life compared to analog systems.
- Connectivity Options: Can connect to smartphones, TVs, and other devices for streaming audio directly to the hearing aids.
Major Differences Between Analog and Digital Hearing Aids
To understand whether digital hearing aids are better than analog, it’s important to compare them across several key factors:
Sound Quality
- Analog Hearing Aids: Analog devices amplify all sounds uniformly, which can be beneficial for individuals who prefer a natural listening experience. However, this uniform amplification can make it difficult to hear speech in noisy environments, as background noise is amplified alongside speech.
- Digital Hearing Aids: Digital devices offer superior sound quality due to their ability to process and filter sounds. They can amplify speech while reducing background noise, making conversations clearer and more enjoyable. Additionally, digital hearing aids can be programmed to match the user’s specific hearing needs, ensuring a more personalized experience.
- Winner: Digital hearing aids provide better sound quality and clarity, especially in complex listening environments.
Noise Reduction
- Analog Hearing Aids: Analog hearing aids lack advanced noise reduction capabilities. While they amplify sound effectively, they don’t differentiate between desirable sounds (like speech) and unwanted noise (like traffic or chatter).
- Digital Hearing Aids: Digital hearing aids excel in noise reduction. They use algorithms to identify and suppress background noise while prioritizing speech. This feature is particularly useful in crowded or noisy settings, such as restaurants or public transportation.
- Winner: Digital hearing aids are far superior in managing background noise.
Customization and Programming
- Analog Hearing Aids: Analog devices offer limited customization. Some models allow users to adjust volume or switch between preset programs, but they lack the ability to fine-tune settings for specific environments or hearing profiles.
- Digital Hearing Aids: Digital hearing aids are very easy to customize as per individual needs. Audiologists can program them to match the user’s unique hearing loss, lifestyle, and preferences. Many digital devices also come with smartphone apps that allow users to adjust settings on the go.
- Winner: Digital hearing aids offer greater flexibility and personalization.
Features and Connectivity
- Analog Hearing Aids: Analog hearing aids are relatively simple devices with few additional features. They focus solely on amplifying sound and don’t include modern conveniences like wireless connectivity.
- Digital Hearing Aids: Digital hearing aids come with a wide range of features, including Bluetooth connectivity, directional microphones, telecoil technology, and rechargeable batteries. Bluetooth-enabled devices can connect to smartphones, TVs, and other audio sources, allowing users to stream sound directly to their hearing aids.
- Winner: Digital hearing aids provide a more feature-rich experience.
Size and Design
- Analog Hearing Aids: Analog hearing aids tend to be larger and less discreet than modern digital devices. Their bulkier design may be less appealing to users who prefer subtle or invisible hearing aids.
- Digital Hearing Aids: Digital hearing aids are available in a variety of styles, including behind-the-ear (BTE), in-the-ear (ITE), and completely-in-canal (CIC) models. Many digital devices are sleek and discreet, making them more aesthetically pleasing.
- Winner: Digital hearing aids offer more options in terms of size and design.
- Cost: Analog Hearing Aids: Analog hearing aids are generally more affordable than digital devices. Their simpler technology and lack of advanced features make them a budget-friendly option for individuals with mild to moderate hearing loss.
- Digital Hearing Aids: Digital hearing aids are more expensive due to their advanced technology and additional features. However, many users find the improved sound quality and functionality worth the investment.
- Winner: Analog hearing aids are more cost-effective, but digital hearing aids offer better value for money in the long run.
- Maintenance and Durability: Analog Hearing Aids: Analog devices are relatively simple and may require less maintenance than digital hearing aids. However, their older technology may not be as durable or reliable over time.
- Digital Hearing Aids: Digital hearing aids are more complex and may require regular software updates or repairs. That said, modern digital devices are built to last and often come with warranties to ensure long-term reliability.
- Winner: Both types of hearing aids have their pros and cons in terms of maintenance, but digital devices are generally more durable.
Advantages of Digital Hearing Aids

- Digital hearing aids have become the preferred choice for most users due to their numerous advantages:
- Enhanced Sound Quality: Digital devices provide clearer and more natural sound by processing and filtering audio signals.
- Noise Reduction: Advanced algorithms reduce background noise, making it easier to focus on speech.
- Customizable Settings: Users can adjust their hearing aids to suit different environments and preferences.
- Modern Features: Bluetooth connectivity, directional microphones, and smartphone apps enhance convenience and usability.
- Discreet Design: Digital hearing aids are available in smaller, more attractive designs.
- Improved Performance: Digital devices adapt to changing environments in real-time, ensuring optimal performance.
Disadvantages of Digital Hearing Aids
- Despite their benefits, digital hearing aids have some drawbacks:
- Higher Cost: Digital devices are more expensive than analog hearing aids, which may be a barrier for some users.
- Complexity: The advanced features and settings can be overwhelming for individuals who prefer simplicity.
- Maintenance: Digital hearing aids may require more frequent updates and repairs.
Advantages of Analog Hearing Aids

- Cost-Effective: Analog hearing aids are generally more affordable, making them accessible to a wider range of people.
- Simple Design: Suitable for individuals who prefer less technological complexity, analog hearing aids have straightforward controls.
- Reliability: They are less prone to software issues and can be more reliable in certain situations.
- Ease of Use: Analog devices are easy to use, with simple volume controls that require minimal adjustment.
Disadvantages of Digital Hearing Aids
- Limited Sound Processing: Analog hearing aids amplify all sounds equally — speech, background noise, and environmental sounds. This makes it hard for the user to focus on specific sounds, especially in noisy environments.
- Lack of Customization: They offer minimal or no digital programming options, so the sound can’t be fine-tuned for different listening situations like digital hearing aids can. This means less personalized hearing experience.
- Noisy Environments Become Challenging: Analog devices don’t have noise-reduction technology. So in places like restaurants or traffic, users often struggle to hear clearly because everything is amplified together.
- No Advanced Features: They lack modern features like Bluetooth connectivity, feedback cancellation, or directional microphones, which are commonly available in digital models.
- Becoming Outdated: As technology advances, analog hearing aids are becoming less available and less supported. Most manufacturers are focusing on digital hearing aids, which means fewer repair and replacement options for analog users in the future.
Digital vs Analog Hearing Aids: What Should You Choose?
Choose Analog Hearing Aids If:
- You have mild to moderate hearing loss and don’t need advanced features.
- You prefer a more natural sound without digital processing.
- You’re looking for a budget-friendly option that meets basic hearing needs.
Choose Digital Hearing Aids If:
- You have moderate to severe hearing loss and need customized amplification.
- You often find yourself in noisy environments and require advanced noise reduction.
- You value modern technology, such as Bluetooth, smartphone apps, and discreet designs.
Still unsure what’s best for you? Visit our clinic for a free hearing aid trial and let our experts help you find the perfect match!
Conclusion of Digital vs Analog Hearing Aids
In most cases, digital hearing aids are better than analog devices due to their superior sound quality, advanced features, and customization options. They offer a more personalized and enjoyable listening experience, making them the preferred choice for many users. However, analog hearing aids may still be a viable option for individuals seeking simplicity and affordability.
Ultimately, the decision between analog and digital hearing aids depends on your specific needs, preferences, and budget. Consulting with an audiologist can help you determine which type of hearing aid is best suited to your hearing loss and lifestyle. Regardless of your choice, both analog and digital hearing aids can significantly improve your quality of life by helping you reconnect with the sounds of the world.