Need Help?
FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions to guide you. If you don't find your question answered here, our support team is just a call or message away. Don't Hesitate to Reach us.
Are hearing loss and dementia related?
Yes, studies have shown a strong connection between hearing loss and dementia. Untreated hearing loss can increase cognitive decline as the brain works harder to process sound, leaving fewer resources for memory and thinking. Social isolation caused by hearing loss can also contribute to cognitive issues.
Are hearing loss and tinnitus related?
Yes, tinnitus (ringing or buzzing in the ears) is often associated with hearing loss. Both conditions can result from damage to the auditory system, including exposure to loud noises, aging, or certain medical conditions.
Can hearing loss be cured?
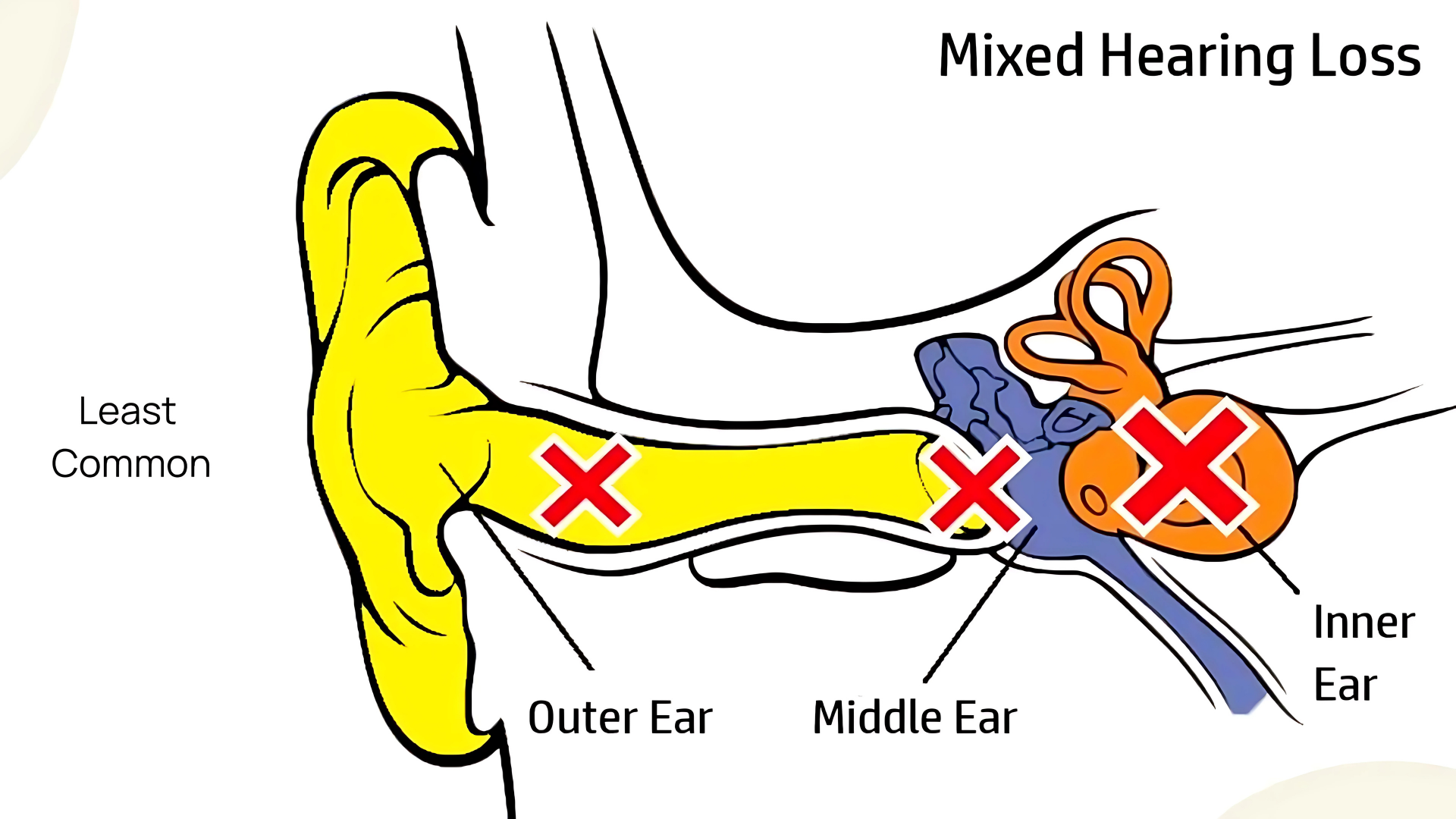
The treatment for hearing loss depends on its cause. Sensorineural hearing loss (caused by damage to the inner ear or nerves) is typically permanent, but it can be managed with hearing aids or implants. Conductive hearing loss (caused by blockages or structural issues) is sometimes treatable with surgery or medication.
Can hearing loss be hereditary?
Yes, hearing loss can be hereditary. Genetic factors may contribute to both congenital hearing loss (present at birth) and progressive hearing loss that occurs later in life.
Can hearing loss be cured in babies?
Some types of hearing loss in babies can be treated or managed, depending on the cause. For example, conductive hearing loss caused by ear infections may be reversible. However, sensorineural hearing loss often requires interventions like hearing aids or cochlear implants.
Can hearing loss from chemo be reversed?
Hearing loss caused by chemotherapy drugs (ototoxicity) is often permanent. However, early detection and protective measures may help minimize damage. Speak with an audiologist if hearing issues arise during treatment.
How does hearing loss occur?
Hearing loss occurs when parts of the auditory system are damaged or impaired. This can result from aging, noise exposure, infections, injuries, certain medications, or genetic factors.
How does hearing loss happen?
Hearing loss happens when sound signals cannot reach the brain properly. This could be due to damage to the ear structures, nerve pathways, or the brain’s ability to process sound.
How is hearing loss measured?
Hearing loss is measured using audiometry tests that assess your ability to hear different pitches and volumes. The results are recorded on an audiogram, showing the degree and type of hearing loss.
How does hearing loss affect the brain?
Hearing loss can lead to changes in the brain’s auditory processing areas, requiring the brain to work harder to interpret sounds. Over time, untreated hearing loss may also impact memory and cognitive function.
How can hearing loss be cured?
While not all types of hearing loss can be cured, many can be managed effectively with treatments such as hearing aids, cochlear implants, surgery, or medication.
How does hearing loss affect daily life?
Hearing loss can impact communication, relationships, work performance, and emotional well-being. It may lead to frustration, social withdrawal, and reduced quality of life if untreated.
What hearing loss requires a hearing aid?
Mild to severe hearing loss often benefits from hearing aids. An audiologist will determine if a hearing aid is appropriate based on the degree of hearing loss and individual needs.
What hearing loss is considered deaf?
Profound hearing loss, where an individual is unable to hear most sounds even with amplification, is generally considered deaf.
What does hearing loss sound like?
Hearing loss often makes sounds seem muffled, unclear, or distorted. High-pitched sounds like birdsong or conversations in noisy environments are typically harder to hear.
What hearing loss qualifies for a cochlear implant?
Individuals with severe to profound sensorineural hearing loss who receive limited benefit from hearing aids may qualify for a cochlear implant. An audiologist and surgeon assess eligibility.
What does hearing loss feel like?
Hearing loss can feel like straining to understand sounds, missing parts of conversations, or experiencing frustration in noisy environments. Some may also feel isolated or anxious.
What hearing loss is considered a disability?
Hearing loss is considered a disability when it significantly impairs an individual’s ability to perform daily tasks or communicate effectively, often determined by hearing thresholds.
Which hearing loss is permanent?
Sensorineural hearing loss, caused by damage to the inner ear or auditory nerve, is typically permanent. It cannot be reversed but can be managed with devices like hearing aids or implants.
Which hearing loss is progressive and associated with aging?
Presbycusis, age-related hearing loss, is progressive and primarily affects high-frequency sounds. It typically occurs due to natural wear and tear on the auditory system.
Why does hearing loss occur?
Hearing loss occurs due to factors like aging, noise exposure, infections, genetic predisposition, certain illnesses, or medications that damage the auditory system.
Why does hearing loss cause dementia?
Hearing loss contributes to dementia by increasing cognitive load, reducing social interaction, and potentially leading to brain changes. These factors can accelerate cognitive decline over time.